Scopus Indexed
Scopus Indexed
Article Peer-Reviewed
Open
Peer Review
Peer Review
Reducing Food Loss and Waste in the Hospitality and Food Service Sector: A Design Thinking Approach
Centre for Design Engineering, Cranfield University, Cranfield, MK43 0AL, United Kingdom
*
For correspondence.
Academic Editor:
Received: 26 December 2023 Accepted: 13 September 2024 Published: 8 November 2024
Abstract
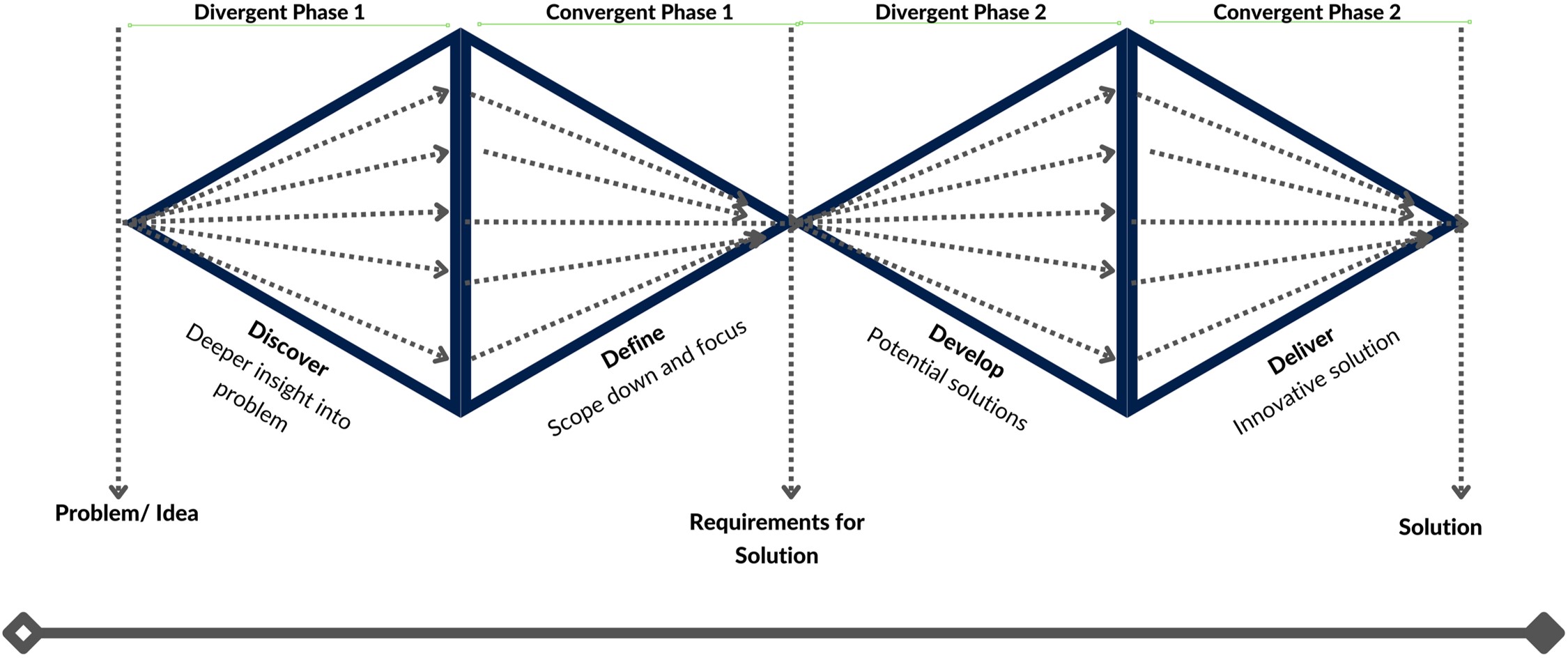
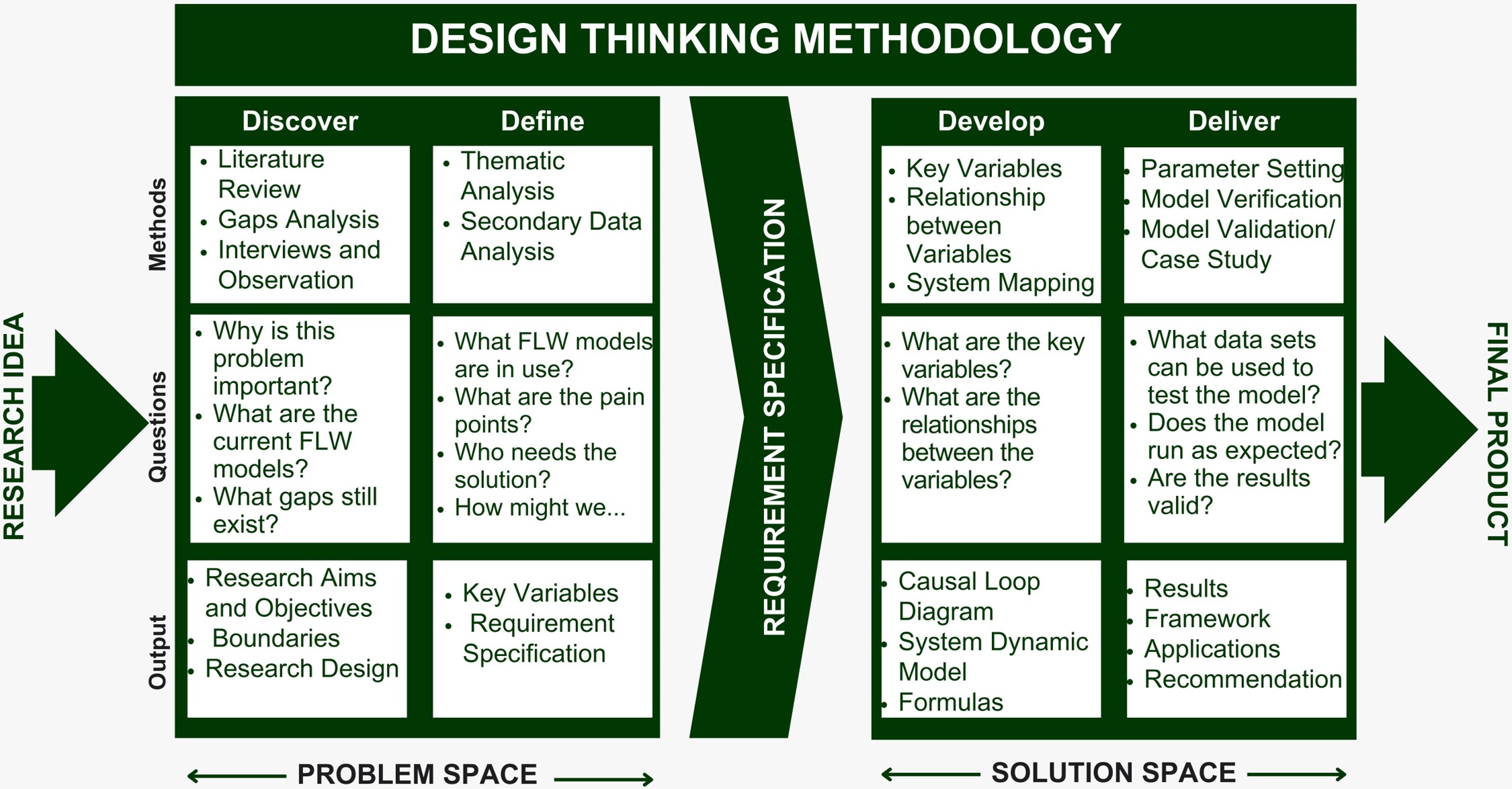
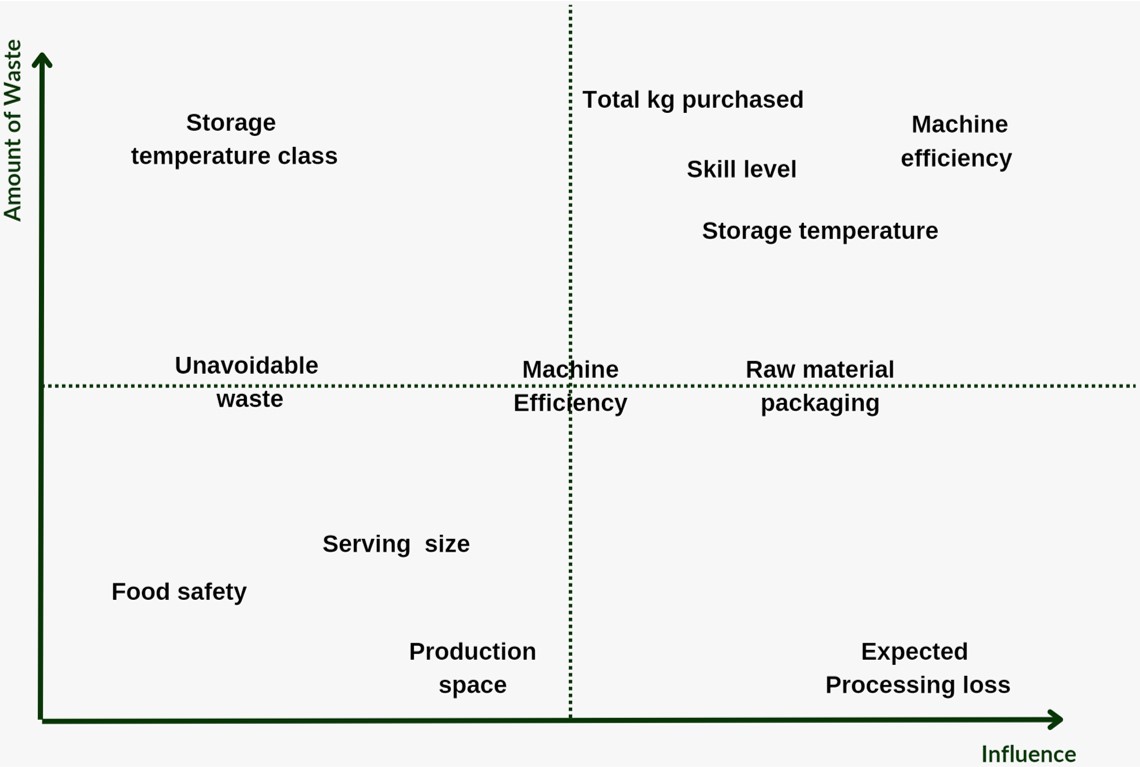
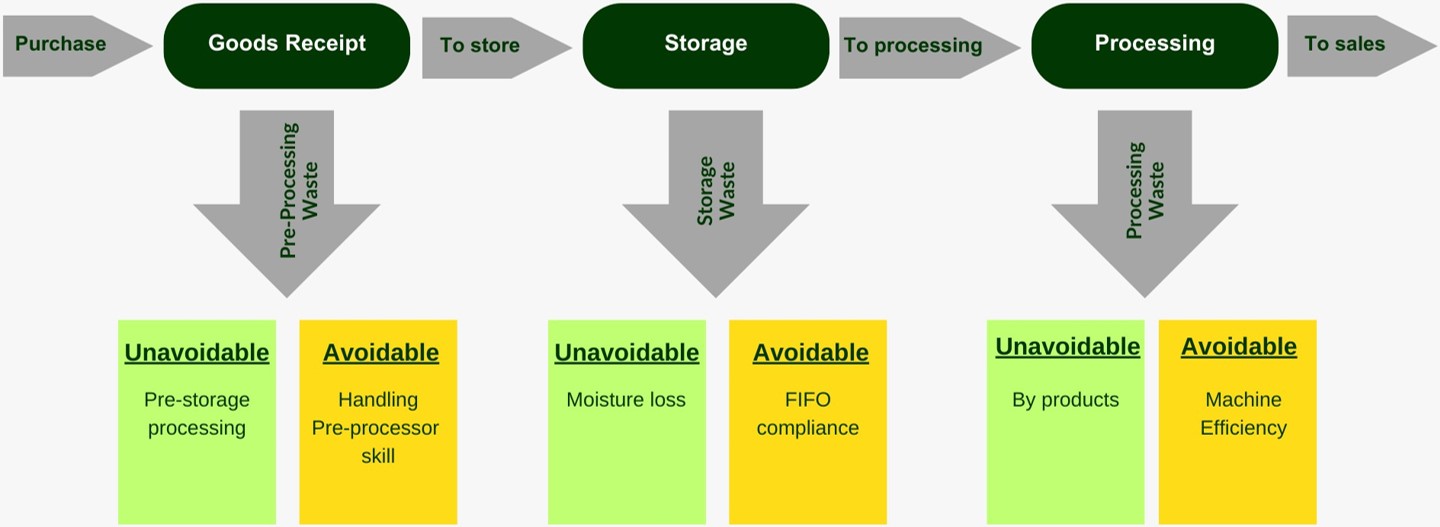
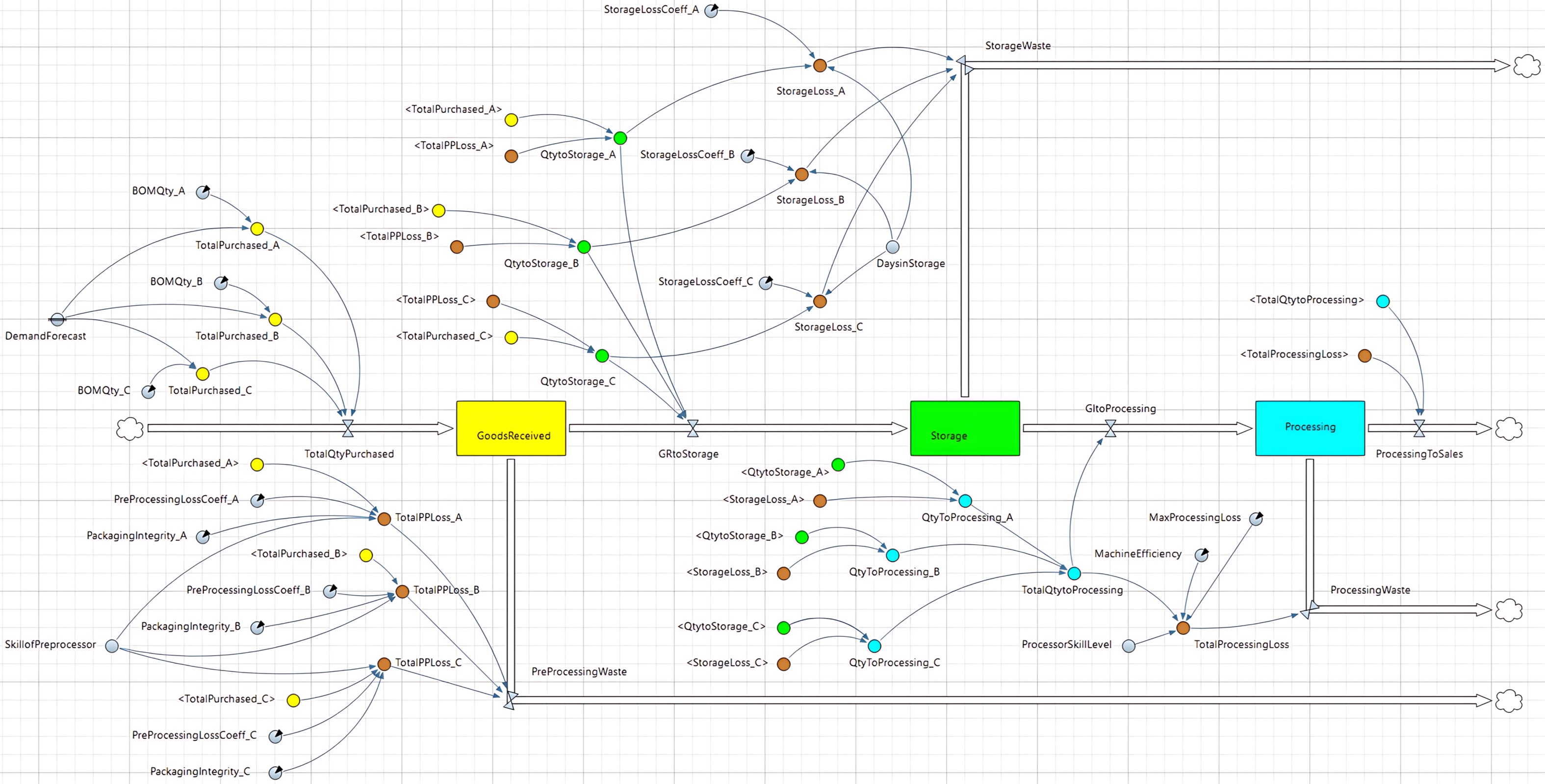
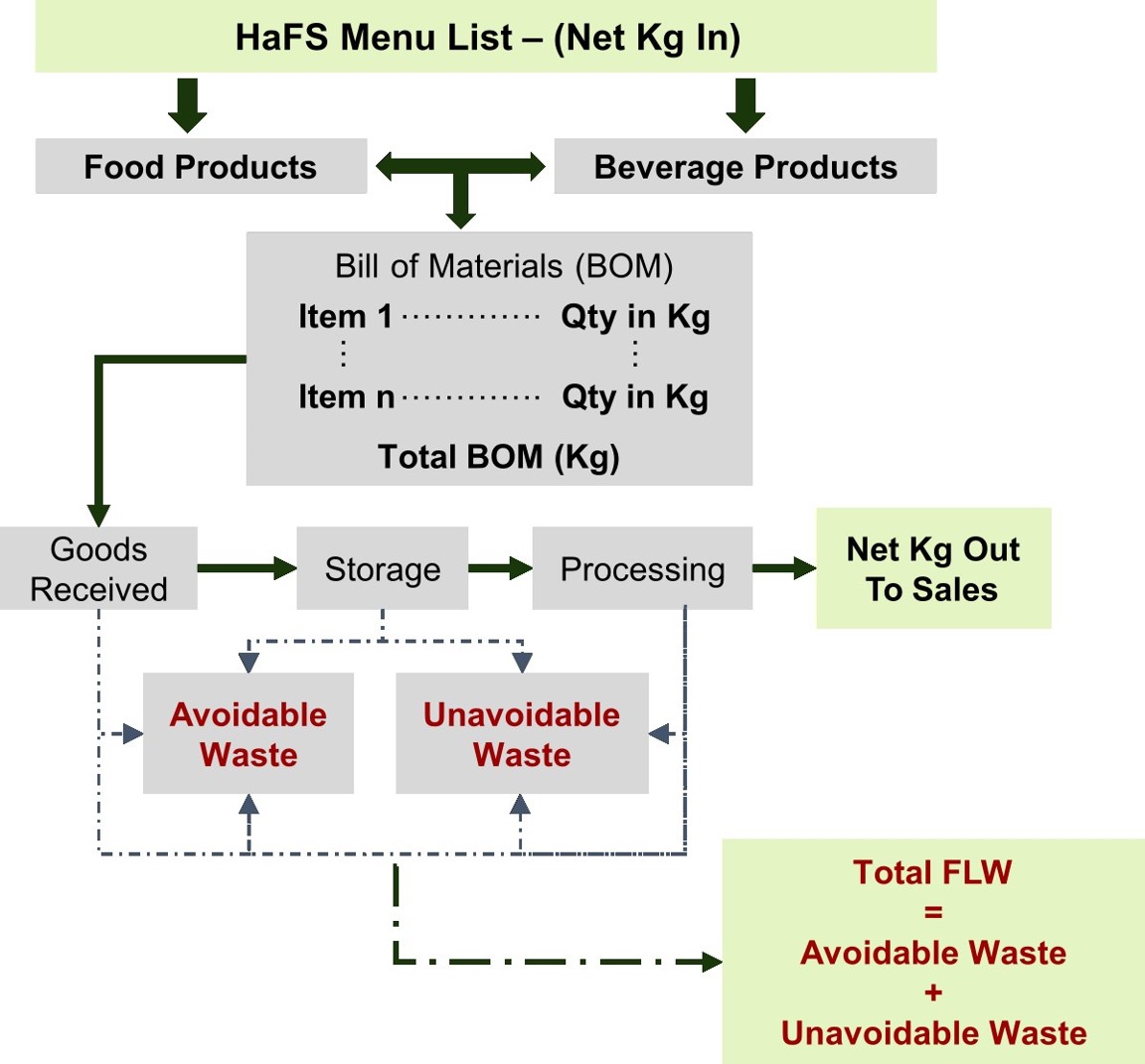
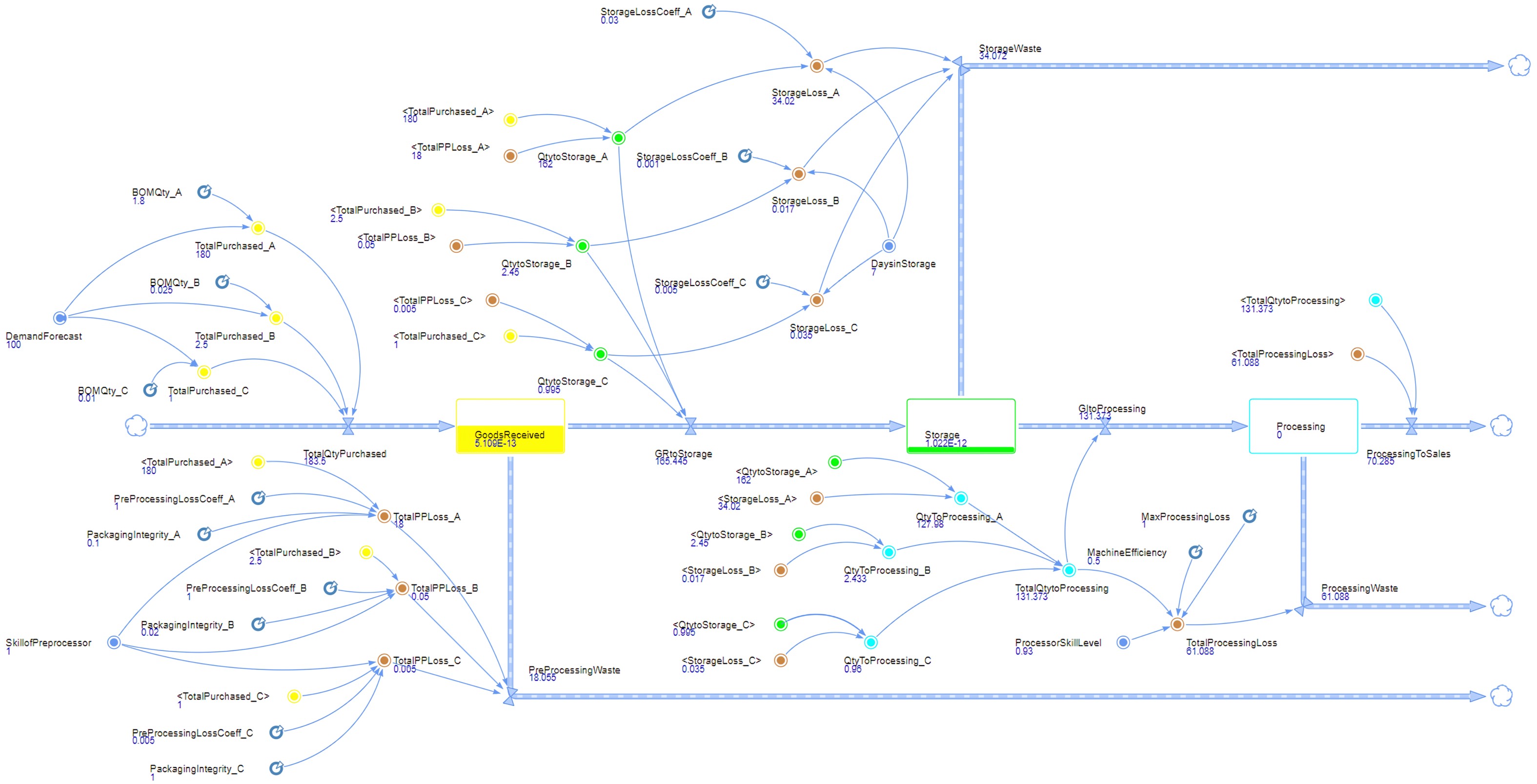
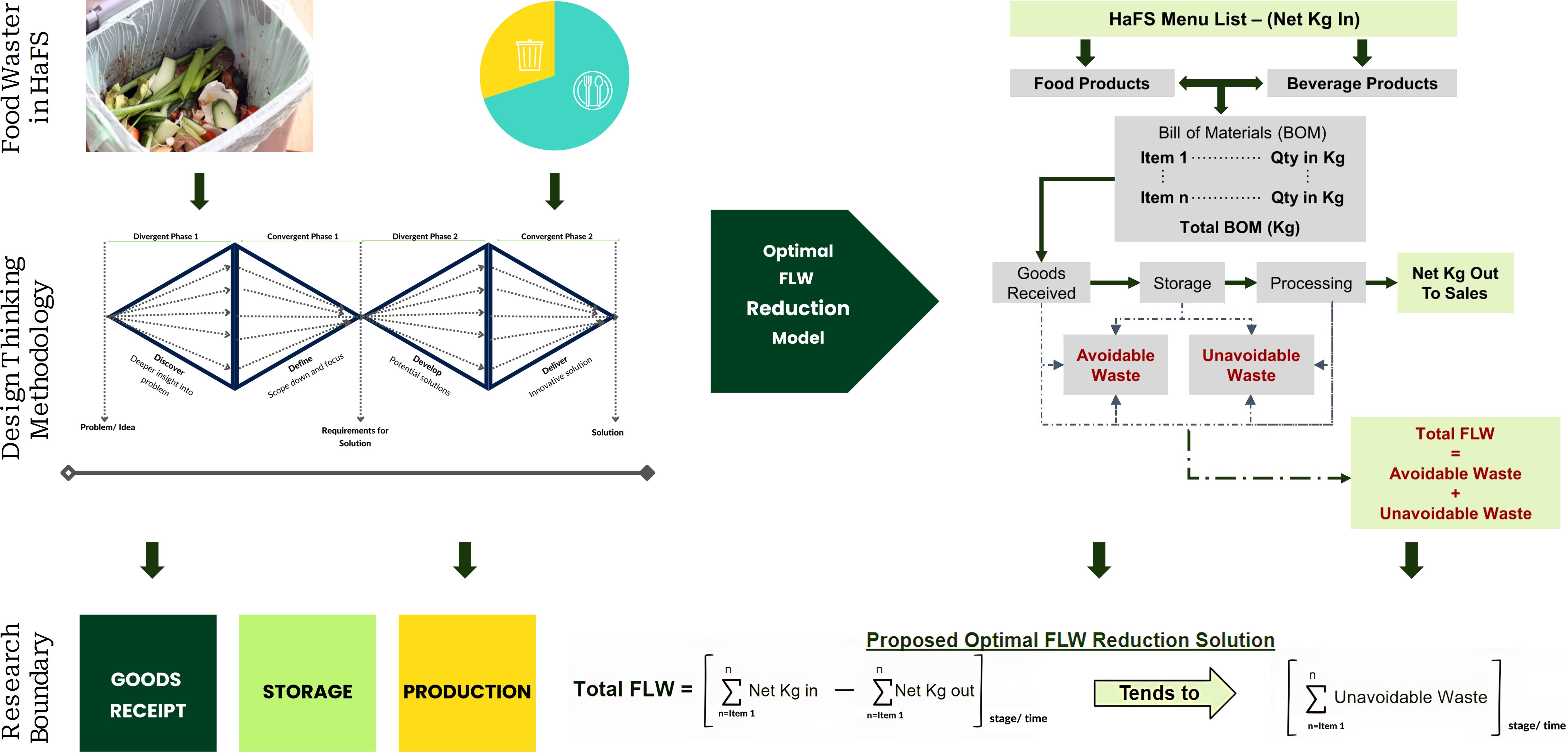
Food loss and waste is a global issue that occurs in all stages of the food supply chain and leads to negative environmental impacts. The Hospitality and Food Service (HaFS) industry is the second largest contributor to food waste. This research investigates the challenges that the HaFS businesses face in adopting sustainable waste reduction strategies using the double diamond design thinking methodology proposed by the UK Design Council. It was discovered that most HaFS businesses do not measure or report on Food Loss and Waste (FLW) due to a lack of clarity on how to do so, complex solutions, low cost-benefit ratios and consequently low motivation. Also, businesses that implement some level of FLW reduction strategies often prioritise post-plate waste and set arbitrary targets which are difficult to achieve sustainably. The research proposes a two-step innovative solution to this problem. The first step involves using a Systems Dynamic (SD) model to represent the complex internal operations in food preparation to reveal its waste hotspots, and to predict the optimal achievable FLW targets within that system. While the second step proposes a system-specific FLW reduction framework based on the SD model parameters that deliver the optimal waste reduction solution.
Graphical Abstract
Figures in this Article
Would you like to reuse the images? Contact the journal editorial office to obtain high-quality versions.
Keywords
food loss and waste; hospitality and food service; design thinking; system dynamics;
FLW measurement and reporting
FLW measurement and reporting
Copyright © 2024
Ezeanaka and Tran. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use and distribution provided that the original work is properly cited.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Cite this Article
Ezeanaka, C., & Tran, T. H. (2024). Reducing Food Loss and Waste in the Hospitality and Food Service Sector: A Design Thinking Approach. Highlights of Sustainability, 3(4), 374–393. https://doi.org/10.54175/hsustain3040021
References
1.
Ishangulyyev, R., Kim, S., & Lee, S. H. (2019). Understanding Food Loss and Waste—why Are We Losing and Wasting food? Foods, 8(8), 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080297
2.
Jeswani, H. K., Figueroa-Torres, G., & Azapagic, A. (2021). The extent of food waste generation in the UK and its environmental impacts. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 26(1), 532–547.
3.
Amicarelli, V., Lagioia, G., & Bux, C. (2021). Global warming potential of food waste through the life cycle assessment: An analytical review. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 91, 106677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2021.106677
4.
Levis, J. W., & Barlaz, M. A. (2011). What Is the Most Environmentally Beneficial Way to Treat Commercial Food Waste? Environmental Science & Technology, 45(17), 7438–7444. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103556m
5.
WRAP. (23 November 2023). Food Surplus and Waste in the UK Key Facts: updated November 2023. https://www.wrap.ngo/resources/report/food-surplus-and-waste-uk-key-facts-updated-november-2023 (accessed 13 April 2024).
6.
Dhir, A., Talwar, S., Kaur, P., & Malibari, A. (2020). Food Waste in Hospitality and Food Services: A Systematic Literature Review and Framework Development Approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 270, 122861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122861
7.
DEFRA. (11 May 2022). Food waste measurement and reporting for food businesses in England. https://consult.defra.gov.uk/environmental-quality/improved-reporting-of-food-waste/supporting_documents/Impact%20Assessment_Improved%20Food%20Waste%20Reporting%202022.pdf (accessed 13 April 2024).
8.
UK Design Council. (n.d.). Framework for Innovation. https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/our-resources/framework-for-innovation (accessed 05 July 2023).
9.
SDG 12 Hub. (2023). Food Loss & Waste. https://sdg12hub.org/sdg-12-hub/see-progress-on-sdg-12-by-target/123-food-loss-waste (accessed18 August 2023).
10.
United Nations. (31 March 2023). SDG indicator metadata - UNSD. https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/metadata/files/Metadata-12-03-01B.pdf (accessed 18 August 2023).
11.
FAO. (2023). SDG Indicators Data Portal: Indicator 12.3.1 - Global Food Loss and Waste. https://www.fao.org/sustainable-development-goals-data-portal/data/indicators/1231-global-food-losses/en (accessed 18 August 2023).
12.
Papargyropoulou, E., Steinberger, J. K., Wright, N., Lozano, R., Padfield, R., & Ujang, Z. (2019). Patterns and Causes of Food Waste in the Hospitality and Food Service Sector: Food Waste Prevention Insights from Malaysia. Sustainability, 11(21), 6016. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11216016
13.
UNEP. (2021). Food waste index report 2021. https://wedocs.unep.org/handle/20.500.11822/35280 (accessed 18 August 2023).
14.
Betz, A., Buchli, J., Göbel, C., & Müller, C. (2015). Food waste in the Swiss food service industry – Magnitude and potential for reduction. Waste Management, 35(35), 218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.09.015
15.
Eastham, J. F., Sharples, L., & Ball, S. (Eds). (2007). Food Supply Chain Management. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780080506678
16.
Enriquez, J. P., Santana, A. H., Espinoza, S. K., & Archila-Godinez, J. C. (2023). Sustainable and healthy food consumption patterns in a multicultural university cafeteria by plate waste visual estimation. Journal of Foodservice Business Research, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15378020.2023.2240206
17.
Lagioia, G., Amicarelli, V., Strippoli, R., Bux, C., & Gallucci, T. (2023). Sustainable and circular practices in the hotel industry in Southern Italy: opportunities, barriers and trends in food waste management. British Food Journal, 126(1), 428–452. https://doi.org/10.1108/bfj-12-2022-1144
18.
European Parliament. (2019). Commission Delegated Decision (EU) 2019/1597 of 3 May 2019 supplementing Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards a common methodology and minimum quality requirements for the uniform measurement of levels of food waste (Text with EEA relevance). http://data.europa.eu/eli/dec_del/2019/1597/oj (accessed 23 August 2023).
19.
Amicarelli, V., & Bux, C. (2020). Food waste measurement toward a fair, healthy and environmental-friendly food system: a critical review. British Food Journal, 123(8), 2907–2935. https://doi.org/10.1108/bfj-07-2020-0658
20.
CEC. (2019). Why and how to measure food loss and waste practical guide. http://www.cec.org/files/documents/publications/11814-why-and-how-measure-food-loss-and-waste-practical-guide-en.pdf (accessed 18 August 2023).
21.
Caldeira, C., De Laurentiis, V., Corrado, S., Van Holsteijn, F., & Sala, S. (2019). Quantification of food waste per product group along the food supply chain in the European Union: a mass flow analysis. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 149, 479–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.06.011
22.
Christ, K. L., & Burritt, R. (2017). Material flow cost accounting for food waste in the restaurant industry. British Food Journal, 119(3), 600–612. https://doi.org/10.1108/bfj-07-2016-0318
23.
Filimonau, V., & Ermolaev, V. A. (2021). A sleeping giant? Food waste in the foodservice sector of Russia. Journal of Cleaner Production, 297, 126705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126705
24.
Tomaszewska, M., Bilska, B., Tul-Krzyszczuk, A., & Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. (2021). Estimation of the Scale of Food Waste in Hotel Food Services—A Case Study. Sustainability, 13(1), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010421
25.
Hjorth, P., & Bagheri, A. (2005). Navigating towards sustainable development: A system dynamics approach. Futures, 38(1), 74–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.futures.2005.04.005
26.
Pankaj, G., & Sepulveda Estay, D. (19–24 July 2020). Review of the application of System Dynamics to problems in food supply chains. The 38th Conference of the System Dynamics Society Virtually, Bergen, Norway.
27.
Azar, A. T. (2012). System dynamics as a useful technique for complex systems. International Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering, 10(4), 377. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijise.2012.046298
28.
Lee, C. K. M., Ng, K. K. H., Kwong, C. K., & Tay, S. T. (2018). A system dynamics model for evaluating food waste management in Hong Kong, China. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 21(3), 433–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0804-8
29.
Oktaviasari, S. A., Vanany, I., & Maftuhah, D. I. (2021). System Dynamic Model for Restaurant’s Food Waste in Surabaya. In The 2nd South American Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management. IEOM Society International. https://doi.org/10.46254/sa02.20210666
30.
Khan, M. Q., Shahid, A., Uddin, M. I., Roman, M., Alharbi, A., Alosaimi, W., et al. (2022). Impact analysis of keyword extraction using contextual word embedding. PeerJ Computer Science, 8, e967. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.967
31.
Mendelow, A. L. (1991). Environmental Scanning: The Impact of the Stakeholder Concept. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Information Systems (pp. 407–418). The Association for Information Systems (AIS).
32.
Thacker, B. H., Doebling, S. W., Hemez, F. M., Anderson, M. C., Pepin, J. E., & Rodriguez, E. A. (2004). Concepts of Model Verification and Validation. Los Alamos National Laboratory. https://doi.org/10.2172/835920
33.
Aviara, N. A., Lawa, A. A., Nyam, D. S., & Bamisaye, J. (2013). Development and performance evaluation of a multi-fruit juice extractor. Global Journal of Engineering, Design and Technology, 2(2), 16–21.
34.
EL-Badry, N., El-Waseif, M., Saed, B., & Ali, H. E. (2014). Effect of Addition Watermelon Rind Powder on the Rheological, Physiochemical and Sensory Quality Attributes of Pan Bread. Middle East Journal of Applied Sciences, 4, 1051–1046.
35.
Juvan, E., Grün, B., & Dolnicar, S. (2023). Waste production patterns in hotels and restaurants: An intra-sectoral segmentation approach. Annals of Tourism Research Empirical Insights, 4(1), 100090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annale.2023.100090
Metrics
Loading...
Journal Menu
Journal Contact
Highlights of Sustainability
Editorial Office
Highlights of Science
Avenida Madrid, 189-195, 3-3
08014 Barcelona, Spain
08014 Barcelona, Spain
Cathy Wang
Managing Editor